0478 Computer Science
Chpater 1 Number System
1.1 Number systems
1.2 Text, sound and images
1.3 Data storage and compression
Chapter 2 Data transmission
2.1 Types and methods of data transmission
2.2 Methods of error detection
2.3 Encryption
Chapter 3 Hardware
3.1 Computer architecture
3.2 Input and output devices
3.3 Data storage
3.4 Network hardware
Chapter 4 Software
4.1 Types of software and interrupts
4.2 Types of programming language, translators and integrated development environments (IDEs)
Chapter 5 The internet and its uses
5.1 The internet and the World Wide Web (WWW)
5.2 Digital currency
5.3 Cyber security
Chapter 6 Automated and emerging technologies
6.1 Automated systems
6.2 Robotics
6.3 Artificial intelligence (AI)
Chapter 7 Algorithm design and problem solving
7.1 The program development life cycle
7.2 Computer systems, sub-systems anddecomposition
7.5 Validation and verification
7.6 Test data
Pseudocode
Chapter 8 Programming
8.1 Programming concepts
8.2 Arrays
pseudocode practice
Mr. Theo
-
+
首页
2.2 Methods of error detection
### Explain how the data might have errors after transmission - Data could be lost - Data could be gained/added - Data could be changed - Bits could be reassembled in the wrong order - Interference could occur - Crosstalk could occur - Data collisions could occur - Data packets could time out/reach their hop count - Network could be infected with malware ### **Parity Checks** - It uses the number of 1-bits in a byte - Type Types - - Even - Even number of 1-bits - Odd - Odd numbers of 1-bits - Example (Even Parity) - | 0 | **1** | **0** | **1** | **1** | **0** | | ---- | ----- | ----- | ----- | ----- | ----- | - The LSB (Left-Most Bit) is the parity bit. As the number of 1s is even, the parity bit would be set to even. #### Describe how the parity bits are used to detect errors - Parity can be set to odd or even - Sender and receiver agree on parity to use - Data is split into bytes // blocks of 7 bytes - Sender counts the number of 1s/0s in each group/byte - Each group/byte is assigned a parity bit to match the parity - Receiving device recounts the number of 1s/0s in each group/byte - ...and compares to parity used/odd/even and if it does not match the parity, an error is reported/identified (in block check) the location of the error(s) can be identified/estimated at the intersection #### Explain how the odd parity check detects errors - The number of 1 s are counted - A parity bit is added to each 7 bits before transmission - … to make the **sum** of the 1s in each byte **odd** - After transmission, if the number is **odd** no error is detected - After transmission, if the number is **even** an error is detected #### Explain how the even parity check detects errors - The number of 1 s are counted - A parity bit is added to each 7 bits before transmission - … to make the **sum** of the 1s in each byte **even** - After transmission, if the number is **odd** an error is detected - After transmission, if the number is **even** no error is detected #### Limitations with Parity Checks - Two bits may change during transmission; therefore error is not found - Even though the parity checks would reveal the errors, the bit(s) changed wouldn’t be identified #### Why a parity check may not detect transmission errors - Transposition error // bits are interchanged - Even number of errors has occurred - it does not check the order of the bits (just the sum of 1s/0s) - even number of bits change - incorrect bits still add up to correct parity • The system could use odd or even parity • A parity bit is added • The data is checked to see if it has incorrect/correct parity ### **Parity Blocks** - To overcome the limitations of parity bits, Parity blocks would be used. - Any changes in bits would be identified through the rows and columns Each row and column where the parity has changed from even to odd should be flagged: 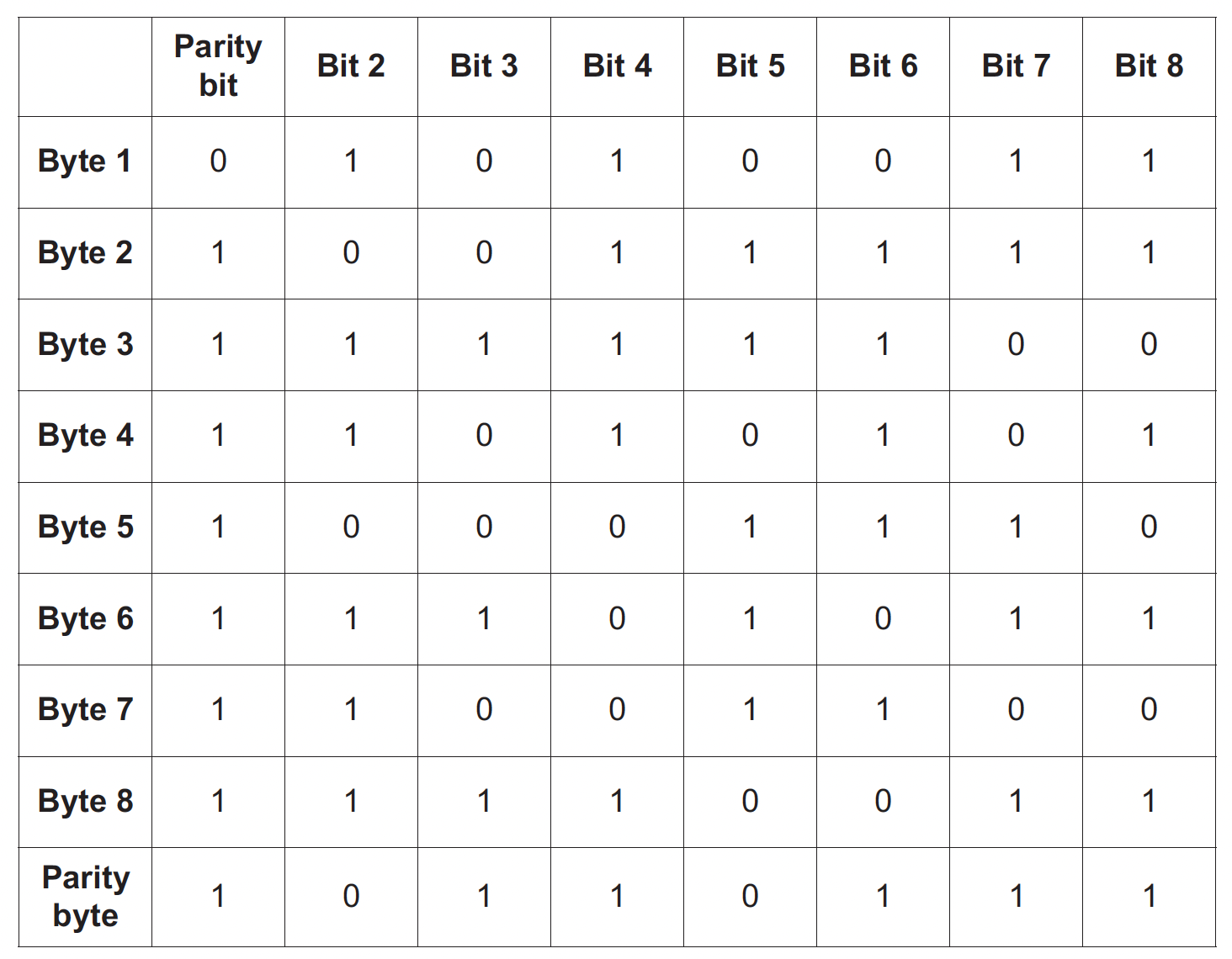 byte 4 (row 4) now has incorrect parity (there are five 1-bits) bit 5 (column 5) also now has incorrect parity (there are five 1-bits). **Explanation** - Counted all the 1s - An even parity has been used - Odd number of ones in that row (byte 4) **and** column (bit 5) ### **Checksum** - Sender calculates a value from the data using an agreed algorithm - Value is appended to the data * Value is transferred with the data * Receiver performs same calculation to recalculate the checksum * Values are compared after transmission, * If the **checksum** **values** do not match, an error is detected, request for data to be resent - If the **checksum** **values** match, no error is detected … ### **Echo Check** - Once the data has been sent, The receiver will send the data back to the sender for verification. - The sender would compare the received and original data for errors. - If the two copies do not match, an error has occurred The only downside is that we wouldn’t know if the error occurred when sending the data or sending the data back for verification. ### **Check Digits** - Digit is calculated from data - Digit is appended / added to data - Digit is recalculated when data has been input - Digits are compared - If digits are different, error is detected // If digits match, no error is detected - Check digits are calculated from all the other digits in the data (ex-codes). The check digit would be the last digit of the code. - These are used to identify mistyping errors such as - - 6372 typed as 6379 - 8432 typed as 842 #### Similarities between the check digit and checksum methods - They both calculate a value from the data - They both append the calculated value to the data - They both recalculate the value - … They both report an error if they don’t match ### **Automatic Repeat Requests (ARQs)** - Uses acknowledgements and timeouts to make sure the user received the data - Check performed on received data // error is detected by e.g. parity check, check sum - If error detected, request is sent to resend data // negative acknowledgement is used - Resend request is repeated till data is sent correctly / requests timeout / limit is reached - Send acknowledgement that data is received // positive acknowledgement is used - If acknowledgement not received in set time data is resent #### Explain how an ARQ operates using a positive acknowledgement method. - Timer is started when sending device transmits a data packet to receiver - Receiving device checks the data packet for errors - Once the receiving device knows the packet is error free it sends an acknowledgement back to the sending device … - … and the next packet is sent - If the sending device does not receive an acknowledgement before the timer ends … - … a timeout occurs - … the data packet is resent … - … until acknowledgement received // until max number of attempts reached #### How parity checks and ARQ operate together to detect and correct errors - Odd or even parity is **set/agreed** for the data - A parity bit is added to each byte of data - … to make the number of 1s match parity - (The first packet of) data is sent and a timer is started - The receiving device counts the number of 1s (in each byte) - If the number of 1s meets parity an acknowledgement is sent to say the data is error free... - the sender then sends the next packet of data and the timer is restarted - If the number of 1s does not meet parity, a negative acknowledgement is sent to the sender that triggers the data to be resent - When the data is sent, a timer is started - If an acknowledgement is not received within the time set, the data is resent ... - … until an acknowledgement is received / resend limit is reached #### Explain why checksum and ARQ are both used. - Checksum used to detect errors (during transmission) - … using a calculated value - ARQ checks if data is received - … uses acknowledgement and timeout - … requests data be sent again if (checksum) detects error / not received
Theo
2026年1月12日 10:55
转发文档
收藏文档
上一篇
下一篇
手机扫码
复制链接
手机扫一扫转发分享
复制链接
Markdown文件
Word文件
PDF文档
PDF文档(打印)
分享
链接
类型
密码
更新密码
有效期