0478 Computer Science
Chpater 1 Number System
1.1 Number systems
1.2 Text, sound and images
1.3 Data storage and compression
Chapter 2 Data transmission
2.1 Types and methods of data transmission
2.2 Methods of error detection
2.3 Encryption
Chapter 3 Hardware
3.1 Computer architecture
3.2 Input and output devices
3.3 Data storage
3.4 Network hardware
Chapter 4 Software
4.1 Types of software and interrupts
4.2 Types of programming language, translators and integrated development environments (IDEs)
Chapter 5 The internet and its uses
5.1 The internet and the World Wide Web (WWW)
5.2 Digital currency
5.3 Cyber security
Chapter 6 Automated and emerging technologies
6.1 Automated systems
6.2 Robotics
6.3 Artificial intelligence (AI)
Chapter 7 Algorithm design and problem solving
7.1 The program development life cycle
7.2 Computer systems, sub-systems anddecomposition
7.5 Validation and verification
7.6 Test data
Pseudocode
Chapter 8 Programming
8.1 Programming concepts
8.2 Arrays
pseudocode practice
Mr. Theo
-
+
首页
2.1 Types and methods of data transmission
## Types and Methods of Data Transmission ### Data Packets - #### Packet Structure - Header - Contains the IP address of the sender and the receiver - The sequence number of the packet - Size of the packet - Payload - Contains the actual data - Trailer - Includes a method of identifying the end of the packet - Error-Checking methods #### Packet Switching - Data is broken/split/divided into packets - Each packet (could) take a different route - A router controls the route/path a packet takes selecting the shortest/fastest available route/path - Packets may arrive out of order - Once the last packet has arrived, packets are reordered - If a packet is missing/corrupted, it is requested again The benefits of packet switching are: » there is no need to tie up a single communication line » it is possible to overcome failed, busy or faulty lines by simply re-routing packets » it is relatively easy to expand package usage » a high data transmission rate is possible. The drawbacks of packet switching include: » packets can be lost and need to be re-sent » the method is more prone to errors with real-time streaming (for example, a live sporting event being transmitted over the internet) » there is a delay at the destination whilst the packets are being re-ordered. ### Data Transmission - *Simplex data transmission* is in one direction only (e.g. computer to printer) 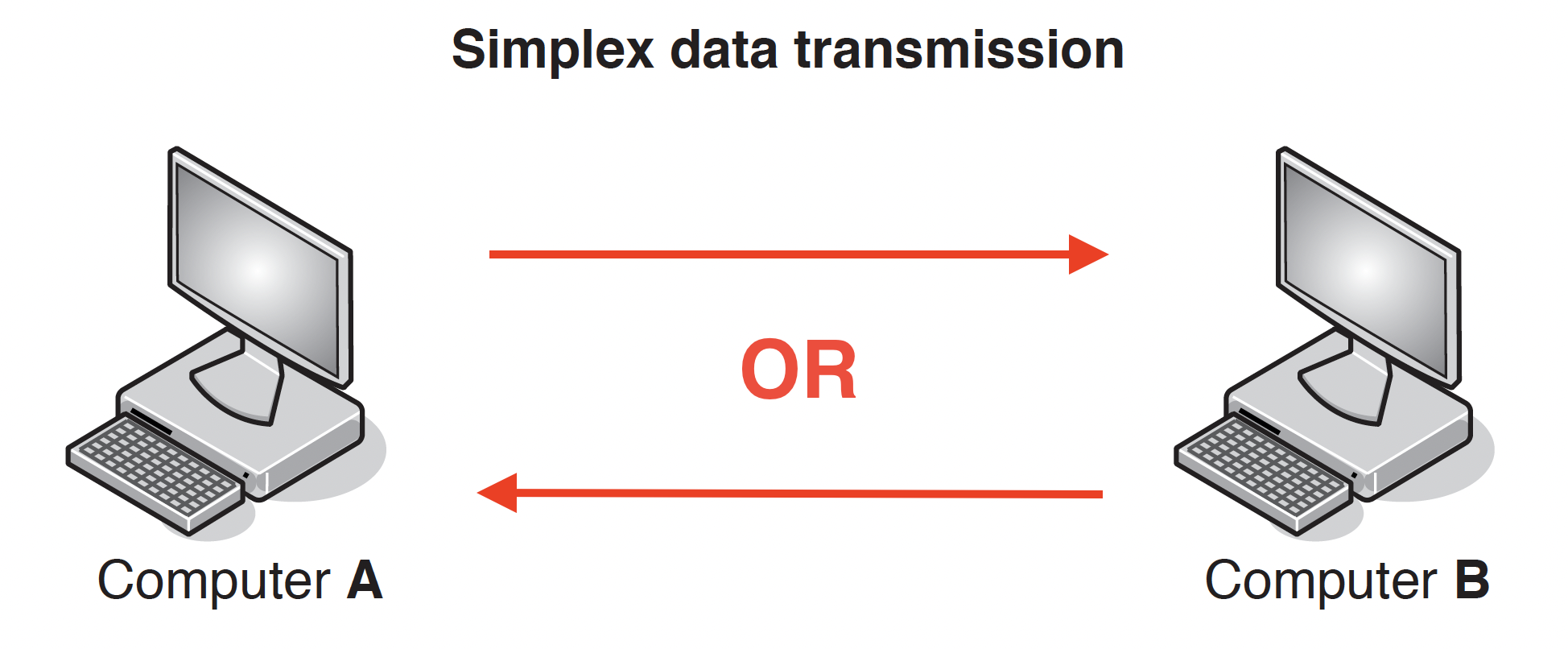 - Benefits - less data collisions碰撞 - Drawback - Data can only be transmitted in one direction. - *Half-duplex data transmission* is in both directions but not at the same time (e.g., in a phone conversation where only one person speaks) - Benefits - Higher bandwidth than full duplex - Drawback - May be more data collisions 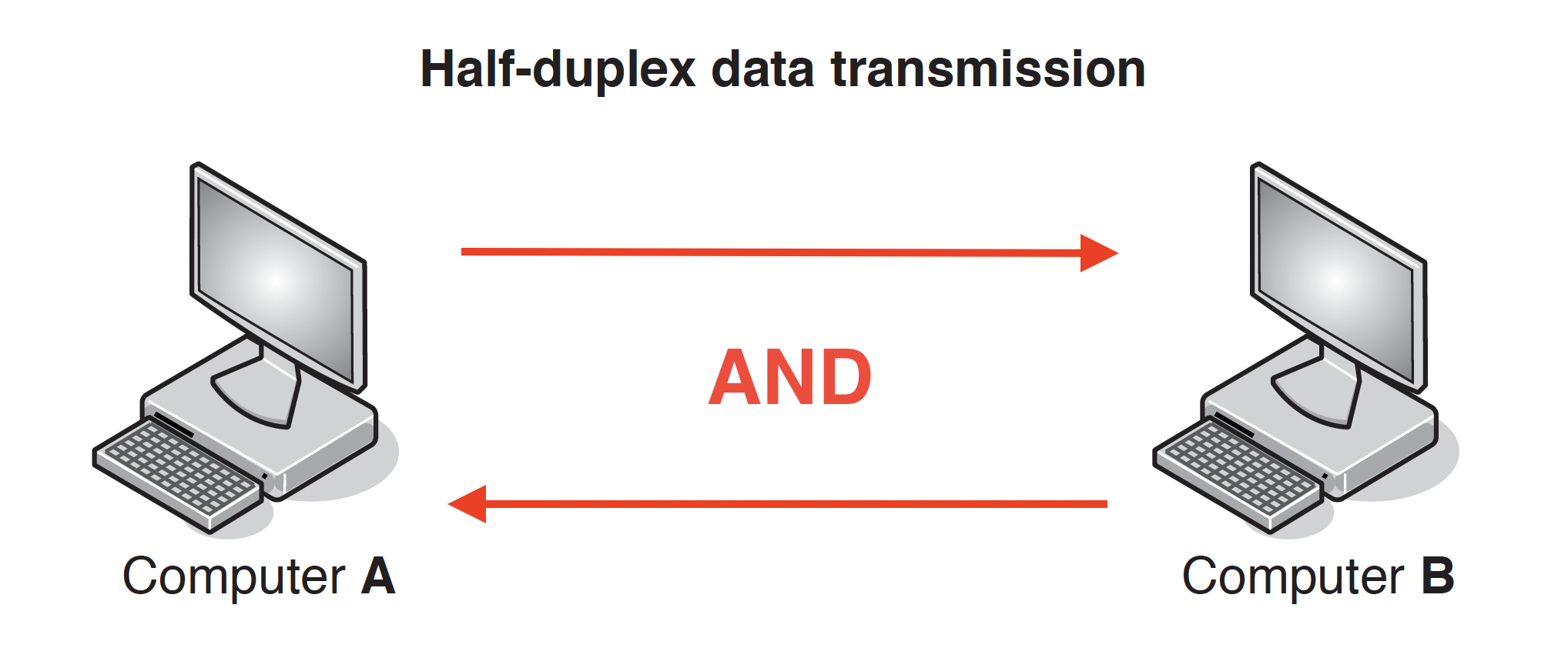 - *Full-duplex data transmission* is in both directions simultaneously同步的 (e.g. broadband connection on the phone line) - Benefits - It sends data in both directions at the same time - … so the devices can send data to each other with no delay - Drawback - More chance of data collisions as data sent in both directions at the same time 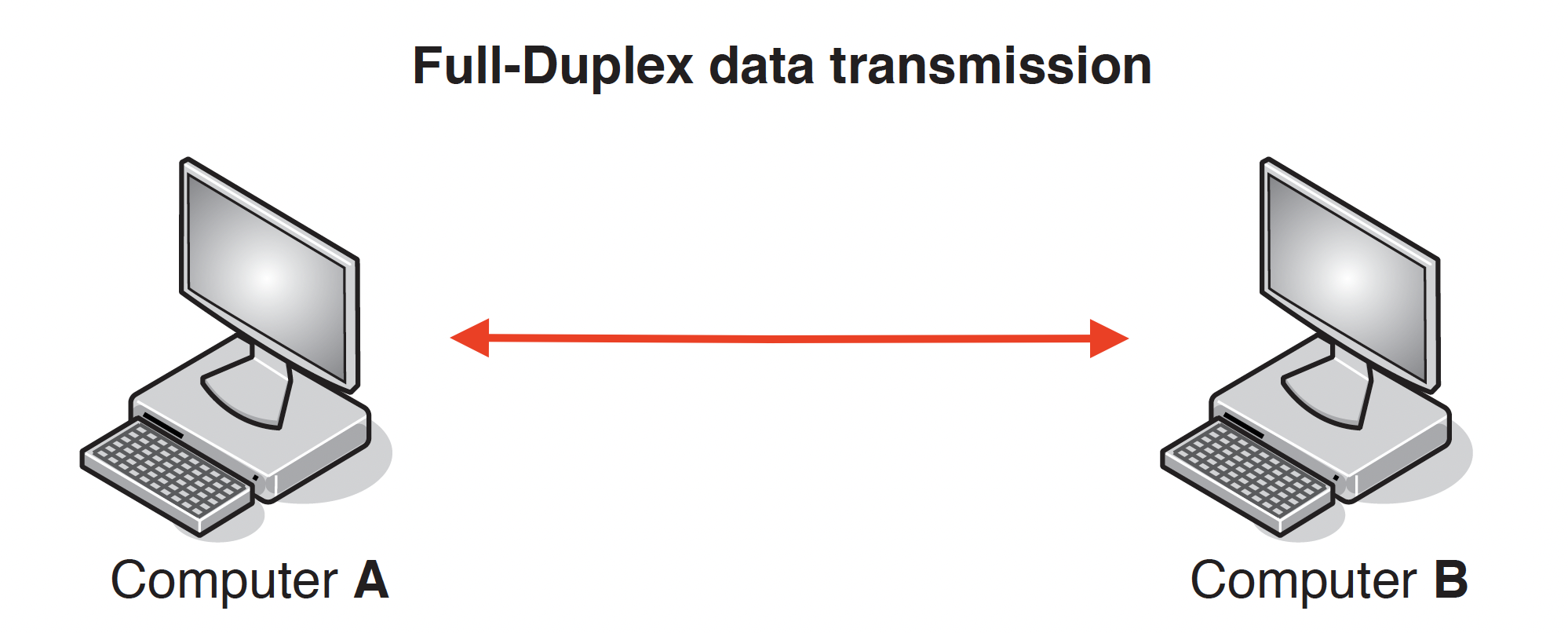 - *Serial data transmission* is when data is sent one bit at a time over a single wire - Benefits - Bits will be arrive in sequence so bits less likely to be skewed - Less crosstalk/interference so less likely to have errors - More accurate/reliable/efficient over long distances - Serial is cheaper to purchase/install/maintain - Drawback - The transmission of data may be relatively slow - Data cannot be sent and received at the same time - Application - sending data from a computer to a printer internal data transfer (buses) - *Parallel data transmission* is when data of several bits are sent down several wires at the same time. - Benefits - It sends multiple bits of data simultaneously using multiple wires - … so the transmission speed of the data will be faster - Drawback - More interference/crosstalk due it to multiple wires - Data may be skewed due to multiple bits at a tie - Application - connect computer to a modem \*skewed (data) – data that arrives at the destination with the bits no longer synchronised \*crosstalk/interference - Crosstalk is the unwanted interference that occurs when a signal transmitted on one communication channel affects a signal in an adjacent channel. ## Universal Serial Bus (USB) - USB is an asynchronous serial data transmission method what is meant by USB - Universal Serial Bus - Uses serial transmission // bits of data are sent one at a time - Universal standard // common interface Benefits One marks per benefit: - It is a universal standard - It can’t be inserted the wrong way around - Supports different transmission speeds - Backward compatible - Automatically detects if correct driver installed - Can power devices - Inexpensive to purchase/manufacture Two marks per benefit: - It is a universal standard - so it is likely to be compatible with the computer - It can only be inserted one way - so there is less chance of connecting a device incorrectly - It is a high-speed connection - so data will be transmitted quicker - It uses serial transmission - so it is cheaper to manufacture/buy - less chance of skewing / errors - It is backwards compatible - so no additional technology is needed - It can power the device - therefore no separate source of power is needed - Device is automatically identified - so no need to find them online / install them manually | Advantages | Disadvantages | | ------------------------------------------------ | ----------------------------------------- | | Automatically detected | Transmission rate is less than 120 MB/sec | | Only fit one way, prevents incorrect connections | Maximum cable length is about 5 metres | | Different data transmission rates | | | Backwards compatible | | | Industry-standard | |
Theo
2026年1月5日 08:27
转发文档
收藏文档
上一篇
下一篇
手机扫码
复制链接
手机扫一扫转发分享
复制链接
Markdown文件
Word文件
PDF文档
PDF文档(打印)
分享
链接
类型
密码
更新密码
有效期