0478 Computer Science
Chpater 1 Number System
1.1 Number systems
1.2 Text, sound and images
1.3 Data storage and compression
Chapter 2 Data transmission
2.1 Types and methods of data transmission
2.2 Methods of error detection
2.3 Encryption
Chapter 3 Hardware
3.1 Computer architecture
3.2 Input and output devices
3.3 Data storage
3.4 Network hardware
Chapter 4 Software
4.1 Types of software and interrupts
4.2 Types of programming language, translators and integrated development environments (IDEs)
Chapter 5 The internet and its uses
5.1 The internet and the World Wide Web (WWW)
5.2 Digital currency
5.3 Cyber security
Chapter 6 Automated and emerging technologies
6.1 Automated systems
6.2 Robotics
6.3 Artificial intelligence (AI)
Chapter 7 Algorithm design and problem solving
7.1 The program development life cycle
7.2 Computer systems, sub-systems anddecomposition
7.5 Validation and verification
7.6 Test data
Pseudocode
Chapter 8 Programming
8.1 Programming concepts
8.2 Arrays
pseudocode practice
Mr. Theo
-
+
首页
5.3 Cyber security
| Candidates should be able to: | Notes and guidance | | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | | 1 Describe the processes involved in, and the aim of carrying out, a range of cyber security threats | Including:<br>– brute-force attack<br>– data interception<br>– distributed denial of service (DDoS) attack<br>– hacking<br>– malware (virus, worm,Trojan horse, spyware, adware, ransomware)<br>– pharming<br>– phishing<br>– social engineering | | 2 Explain how a range of solutions are used to help keep data safe from security threats | Including:<br>– access levels<br>– anti-malware, including anti-virus and anti-spyware<br>– authentication (username and password, biometrics, two-step verification)<br>– automating software updates<br>– checking the spelling and tone of communications<br>– checking the URL attached to a link<br>– firewalls<br>– privacy settings<br>– proxy-servers<br>– secure socket layer (SSL) security protocol | ### brute-force attack - Try to **find** **out**/**guess** a **password** by **repeatedly** entering different **combinations/passwords** - Could use **software** to do it **automatically** #### prevent - **Strong** passwords // passwords that are long and have a combination of letters, numbers and symbols - Two-step verification // two-factor authentication - Biometric password - Limiting the number of login attempts ### DDoS attack - A very large number of emails are sent to a server/network at the same time - …crashing the server/network #### aim of DDoS attack To disrupt the operation of a web server/network - Revenge - To affect a company's reputation 名誉 - Entertainment value娱乐价值 - To demand a ransom勒索 to stop it - To test a system's resilience The attacker encourages people to download Malware onto their computer. This will turn each computer into a bot ,creating a network called a botnet. When the attacker wants the DDoS to take place, repeated requests are simultaneously sent from the computers to a web server. This causes it to crash, meaning that users can no longer access the website that is stored on this hardware. 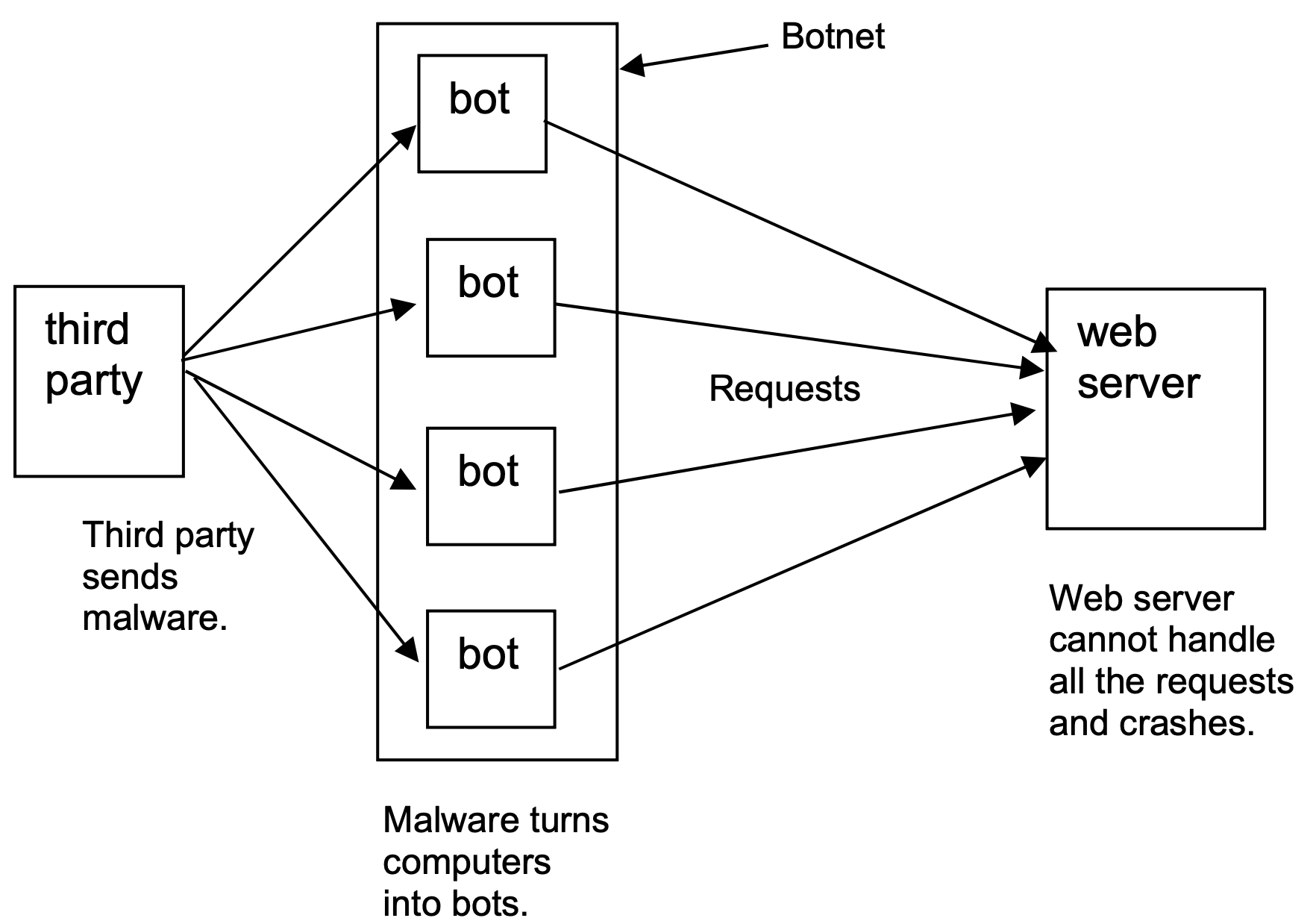 #### prevent - Proxy server - Firewall - Users scanning their computers with anti-malware ### Data Interception - Data is being sent from one device to another - The data is being examined during transmission - Packet sniffer嗅探器 is used - Intercepted data is reported to a third-party during transmission and analysed for anything useful - Connection hacked to spoof destination address 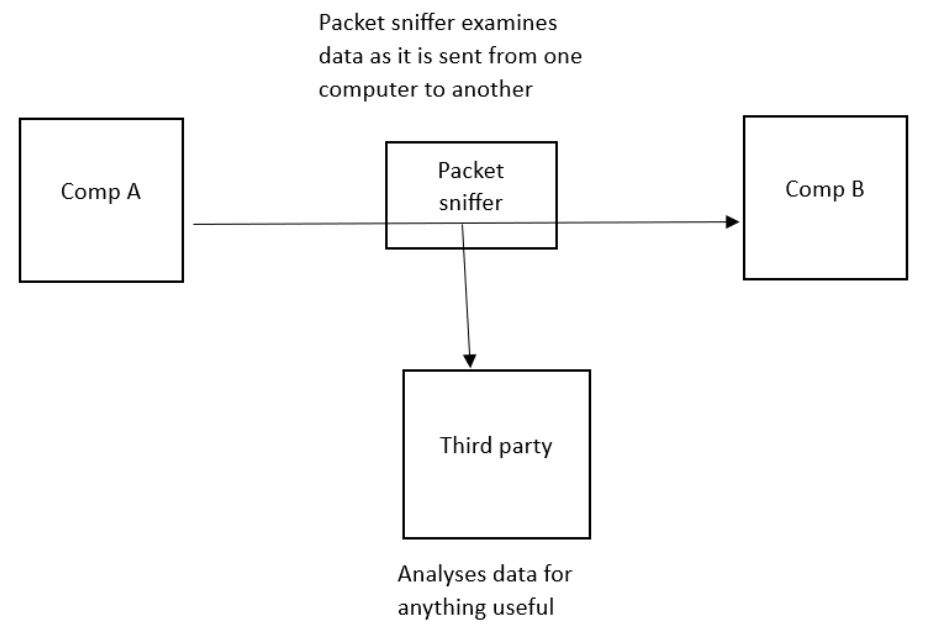 #### Prevent Encryption if the data is intercepted it will be **meaningless** (because they do not have the decryption key) ### Hacking Gaining unauthorised access to a computer #### Virus • Software/code that replicates • …when the user runs it // with an active host • Deletes/damages/corrupts data/files // takes up storage/memory space #### Worm • Software/code that replicates itself on a **network** • without active host • Takes-up bandwidth • Deletes/damages/corrupts data/files // takes up storage/memory space • Opens back doors to computers over the network • Used to deposit other malware on networked computers #### Trojan horse • Software/code that is hidden within other software // Software that is disguised as authentic software • …when **downloaded/installed** the other **malware**/**by example** it contains is **installed** #### Adware • Software/code that generates/displays (unwanted) adverts on a user's computer • Some may contain spyware/other malware • Some when clicked may link to viruses • Reduces device performance // reduces internet speed • Redirects internet searches/user to fake websites #### Ransomware • Software/code that stops a user accessing/using their computer/data • …by encrypting the data/files/computer • A **fee** has to be paid to decrypt the data // A **fee** has to be paid to 'release' the computer/device/data ### Spyware - Malicious software // type of malware - Tracks / records keypresses // keylogger - Sends data to third party - Collected data is analysed to obtain data ### Prevents spyware: 1. Drop-down boxes // virtual keyboard • Means key logger cannot collect data 2. Only requires part of the password • Hacker doesn’t get the full password 3. Two-step verification // Two-factor authentication • Extra data is sent to device making it more difficult for hacker to obtain it • if attempted from a remote location, it will not be accepted 4. Use a biometric device • The person's biological data (e.g. their fingerprint) is also required #### Phishing - Legitimate looking email sent to user - Clicking on link/attachment takes user to fake website - Asked to reveal/designed to steal sensitive information ##### purpose - To obtain a user’s personal data ##### Prevent - checking Spelling and Tone in communications - Check - If there is spellinnngngs errors in the email - The tone used in the email message - checking the URL attached to a link #### Pharming - Malicious code/malware is installed on user’s computer without users' knowledge - Redirects (correct URL) to different/fraudulent website - Asked to reveal/designed to steal sensitive information ##### purpose - To obtain a user’s personal data ##### similarities and differences between phishing and pharming Similarities: - Both are designed to steal personal data - They both pose as a real company/person Differences: - Pharming uses malicious code installed on hard drive - Phishing is in form of an email - Phishing requires use to follow a link / open an attachment #### Spam - Junk / unwanted email - Sent to large numbers of people - Used for advertising / spreading malware - Fills up mail boxes #### social engineering - Manipulating / deceiving / tricking people ... - ... to obtain data // to force them to make an error - Five common types of threat: - Instant messaging (malicious link embedded in message) - Scareware (tell you that your computer is infected with virus) - Email (genuine looking emails) - Baiting (leave a pendrive where it can be found) - Phone calls (asks you to download special software) - All threats above are effective methods for introducing malware. #### Access Level - Providing users with different permission for the data - Limiting access to reading data limiting the data that can be viewed - Limiting access to editing data // limiting the data that can be deleted / changed - Normally linked to a username #### Anti-virus (software) // Anti-malware (software) • Scans the computer system (for viruses) • Has a record of known viruses • Removes/quarantines any viruses that are found • Checks data before it is downloaded • and stops download if virus found/warns user may contain virus #### Authentication ##### username and password Passwords • Making a password stronger // by example • Changing it regularly • Lock out after set number of attempts // stops brute force attacks // makes it more difficult to guess ###### Increases security - Make the password require more characters - Makes the password harder to crack/guess - More possible combinations for the password - Make the password require different types of characters - Makes the password harder to crack/guess - More possible combinations for the password ##### biometric password - It uses characteristics/features that belong to a human ###### why a biometric password is more secure - A biometric password cannot be guessed - It is very difficult to fake a biometric password - A biometric password cannot be recorded by a keylogger/spyware - A perpetrator cannot shoulder surf to see a biometric password ##### Two-step verification // Two-factor authentication - Requires two methods of authentication to verify who a user is. - Example: Online shopping - Step 1: Enter user name and password - Step 2: Enter PIN that is sent back to her either in an email or as a text message to her mobile phone ###### benefits • Extra data is sent to device, pre-set by user • making it more difficult for hacker to obtain it • Data has to be entered into the same system • so if attempted from a remote location, it will not be accepted #### Automating Software Updates - This ensures that applications like operating systems, anti-virus and other commonly used pieces of software are always operating with the latest version installed. - Greater threats are constantly evolving and that anti-virus companies are always attempting to stay up to date with new attacks. #### Firewall - Criteria can be set (for traffic) - ... such as a blacklist/whitelist (of IP addresses) - It will examine traffic coming into the network - It will check that the traffic meets the set criteria - ... and will reject it if it does not meet criteria - Certain ports used by hackers can be blocked/closed 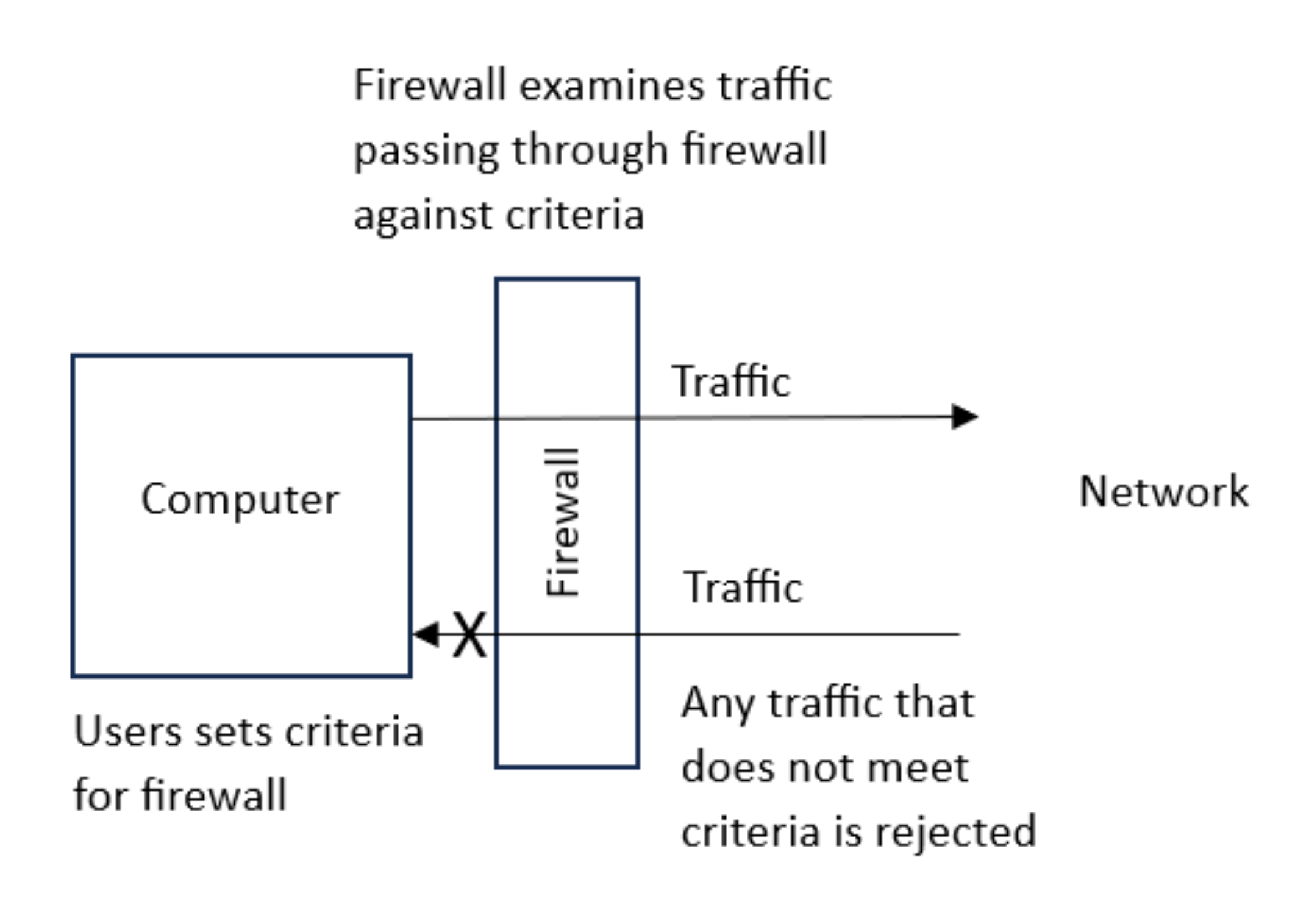 ### Proxy server Can limit the number of requests sent to the web server at a time Can process common requests that will not need to enter the network Act as a firewall Examine incoming data to the webserver/network Can have set rules/criteria for data to meet Can have a blacklist/whitelist/list of IP addresses to block Blocks traffic that doesn’t meet criteria Closing certain ports #### protect against - DDoS // DoS - Hacking - Malware // by example - Brute-force attack ##### similarities and difference between proxy servers and firewalls Similarities • Check incoming and outgoing signals // filter traffic • Store whitelist/blacklist • Block incoming/outgoing signals • Both block unauthorised access • Keep a log of traffic • Both can be hardware or software (or both) Differences • Proxy can hide user's IP address, firewall does not hide the user's IP address • Proxy intention is to divert attack from server, firewall is to stop unauthorised access • Proxy protects a server, firewall protects individual computer • Proxy examines/processes requests for a website but a firewall does not (checks type of signal) // Proxy **processes** client-side requests whereas firewall **filters** packets • Proxy transmits website data to the user, but a firewall does not (it allows valid signals) • Proxy allows faster access to a web page using cache, but a firewall does not (allow faster access or have cache) • Proxy can hide internal network from internet, but a firewall cannot ##### Identify two tasks that can be performed by a proxy server that are not performed by a firewall - Hide a public IP address - Caching #### Privacy settings - Privacy settings are the controls available on web browsers, social networks and other websites that are designed to limit who can access and see a user’s personal profile. - Examples: - "Do not track" setting - Allow payment method to be saved (avoid the need to key in information everytime, which is dangerous) - Safer browsing - App (sharing of location) ### how a secure connection is created using the SSL protocol • Encrypted connection established using asymmetric encryption • to make any data sent meaningless • The **web** **browser** asks the **web** **server** to identify itself by sending its digital certificate. • The digital certificate is authenticated/validated by the **web** **browser**. • If the certificate is authenticated, the connection is secure/the transaction can begin. • If the certificate is not authenticated, the transaction is cancelled. ### how the SSL protocol secures the data for transmission - It encrypts it - Uses digital certificates ### the process of SSL and how it provides a secure connection - SSL is a (security) protocol - It encrypts any data that is sent - It uses digital certificates which is sent to the user’s browser that contains the website's public key - The digital certificate can be used to authenticate the website - Once the certificate is authenticated, the transaction will begin HTTPS - Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure - It is a protocol that is a set of rules/standards - Secure version of HTTP - Secure website // secures data - Uses TLS / SSL - Uses encryption ### Benefits of ssl Data if intercepted cannot be understood // Data is encrypted // Data is scrambled // uses keys to encode/decode data ## Check if the web is secure Locked padlock HTTPS View the certificate ### Transport Layer Security (TLS) - A more modern and more secure version of SSL. It is a form of protocol that ensures the security and privacy of data between devices and users when communicating over a network ## Process of TLS Client/browser requests secure connection to server Client/browser requests the server to identify itself Server provides a digital certificate Client/browser validates the certificate Client/browser send signal back to server (to begin transmission) A session key is generated Encryption method is agreed // data is encrypted ## The Two Layers of TLS Handshake (layer) Record (layer) ## Describe the purpose of the handshake layer Carries out authentication of server and client Handles encryption algorithms / keys ##### How browser checks that the website is secure - requests web server to identify itself // request to view the (SSL) certificate - receives a copy of the (SSL) certificate, sent from the webserver - checks if (SSL) certificate is authentic/trustworthy - sends signal back to web server that the certificate is authentic/trustworthy
Theo
2025年11月30日 14:35
转发文档
收藏文档
上一篇
下一篇
手机扫码
复制链接
手机扫一扫转发分享
复制链接
Markdown文件
Word文件
PDF文档
PDF文档(打印)
分享
链接
类型
密码
更新密码
有效期