0478 Computer Science
Chpater 1 Number System
1.1 Number systems
1.2 Text, sound and images
1.3 Data storage and compression
Chapter 2 Data transmission
2.1 Types and methods of data transmission
2.2 Methods of error detection
2.3 Encryption
Chapter 3 Hardware
3.1 Computer architecture
3.2 Input and output devices
3.3 Data storage
3.4 Network hardware
Chapter 4 Software
4.1 Types of software and interrupts
4.2 Types of programming language, translators and integrated development environments (IDEs)
Chapter 5 The internet and its uses
5.1 The internet and the World Wide Web (WWW)
5.2 Digital currency
5.3 Cyber security
Chapter 6 Automated and emerging technologies
6.1 Automated systems
6.2 Robotics
6.3 Artificial intelligence (AI)
Chapter 7 Algorithm design and problem solving
7.1 The program development life cycle
7.2 Computer systems, sub-systems anddecomposition
7.5 Validation and verification
7.6 Test data
Pseudocode
Chapter 8 Programming
8.1 Programming concepts
8.2 Arrays
pseudocode practice
Mr. Theo
-
+
首页
3.1 Computer architecture
## Computer Architecture & Von Neumann architecture The central processing unit (CPU) (also known as a microprocessor or processor) is central to all modern computer systems ##### the purpose of a core in the CPU - To perform a fetch-decode-execute cycle - To process / execute an instruction ##### the purpose of the CPU - It processes data - It processes/executes instructions - It carries out calculations - It carries out logical operations - perform fetch-decode-execute cycles The CPU consists of the following architecture: ##### Control Unit: A component in the CPU that manages the flow of data around the CPU - Fetches each instruction in turn and manages their execution - Handles all processor control signals. - It directs all input and output flow, fetches code for instructions and directs them ##### Arithmetic Logic Unit: - Carries out calculations - Carries out logical operations - Holds temporary values during calculations - in a register called the accumulator (ACC) ##### System Clock: It controls the number of fetch-decode-execute cycles that are performed per second. - produce timing signals/clock pulses on the control bus to ensure the synchronization take place - to keep track of the date and time / timestamp files - to process operations in the correct order / sequence ##### Busses: - To connect the internal components of CPU - Pathway for transmitting data and instructions ###### Address bus - Transmit / carries addresses between components in the CPU - Data travels in only one direction (unidirectional) ###### Control Bus - Transmits control signals from the control unit to other components in the CPU - can be unidirectional or bidirectional ###### Data Bus - Transmit / carries data between components in the CPU - data can travel in both directions ##### Immediate Access Store: - holds all the data and programs that the CPU needs to access - CPU takes data and programs held in backing store and puts them in IAS temporarily - This is done because read/write using IAS is faster compared to the backing store - The IAS is another name for primary (RAM) memory. ##### Registers - A component in the central processing unit (CPU) that is used to temporarily store data. ###### Memory Data Register(MDR) - holds the data/instructions which has been read from or is to be written to the address in the MAR ###### Memory Address Register(MAR) - holds address in memory from which data will be read / to which data wil be written ###### Program Counter (PC) - to store the address / location / memory location of the next instruction to be fetched ###### Index Register (IX) - to store a value that is added to an address to give another address ###### Status Register (SR) - to store flags which are set by events // from the results of arithmetic and logic operations and interrupt flags ###### Program Counter(PC) - Increments the value of the instructions by 1 and also fetches the data and instructions. ###### Current instructions Register(CIR) - Data gets executed from here by sending to bios or processed by sending to ALU ###### Accumulator - stores the result of interim calculations // during calculations data is temporarily held in it 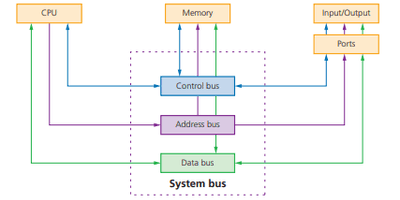 ## The Fetch-Execute Cycle ###### Three stages - Fetch - Decode - Execute ###### Opreation 1. PC contains address of the next instruction to be fetched 2. This address is copied to the MAR via the address bus 3. The instruction of the address is copied into the MDR temporarily 4. The instruction in the MDR is then placed in the CIR 5. The value in the PC is incremented by 1, pointing the next instruction to be fetched 6. The instruction is finally decoded and then executed ### Stored program concept: - Instructions and data stored in the main memory - Instructions fetched and executed in order ### Memory Concept - A computer’s memory is divided in partitions : Each partition consists of an address and its contents e.g. | MEMORY LOCATION | CONTENT | | --------------- | -------- | | 10101010 | 01010110 | ##### Instruction Set An instruction set is a list of all the commands that can be processed by a CPU and the commands are machine code #### Performance of Computer System Factors ##### Bus Width - Determines number of bits that can be simultaneously transferred - Refers to number of lines in a bus - **Increasing bus width increases number of bits transferred at one time, hence increasing processing speed and performance since there** ##### Clock speed - Each instruction is executed on a clock pulse // one F-E cycle is run on each clock pulse - …. so the clock speed dictates the number of instructions that can be run per second - **The faster the clock speed the more instructions(F-E cycles) can be run per second** ##### Number of cores This is a processing unit within the CPU that can fetch, decode and execute instructions. - Each core processes one instruction per clock pulse - **More/multiple cores mean that sequences of instructions can be split between them** - **so more sequences of instructions can be run at the same time** - More cores decreases the time taken to complete task ##### Cache Memory It stores frequently used data/instructions - Commonly used instructions are stored in the cache memory area of the CPU. - **the higher capacity the more frequently used instructions it can store for fast access** ## Embedded System - An embedded system is a combination of hardware and software which is designed to a perform dedicated/single function ### Characteristics - Performs a single/limited/dedicated function/task - It has a microprocessor - It has dedicated hardware - Uses firmware - It is normally built into a larger device/system - User normally cannot reprogram - It does not require much power - It is cheap to manufacture - Works automatically // works without human intervention - It is small (in size) - It is a real-time system ### Examples: - security light system - freezer - vending machine - Set-top box - Motor vehicles
Theo
2025年9月15日 08:29
转发文档
收藏文档
上一篇
下一篇
手机扫码
复制链接
手机扫一扫转发分享
复制链接
Markdown文件
Word文件
PDF文档
PDF文档(打印)
分享
链接
类型
密码
更新密码
有效期